Master of Science in Electrical Engineering MS (EE)
Program Overview
The world is rapidly progressing, and technology has become an essential part of our lives. Electrical Engineering is a field that plays a crucial role in shaping the technology of today and tomorrow. With new innovations emerging every day, pursuing a Master of Science in Electrical Engineering can open doors to several opportunities in this exciting field. The MS Electrical Engineering of the EE Department offers a comprehensive and advanced program in Electrical Engineering. The Electrical Engineering program at EE Department offers students opportunities to work on cutting-edge research projects, gain experience of addressing the real-world problems in their research and develop a professional network at national as well as international level that prepares them for global careers. Graduates of this program are well-equipped to pursue a variety of career paths in related fields both in Pakistan and around the world.
The primary objective of our graduate programs is to impart education and training to a student in interest for pursuing graduate studies, to inculcate the spirit of learning in the student, and enhance his/her research orientation, critical thinking, research analysis capabilities, hypothesis testing and report writing skills. The following streams are offered in the program.
Research Opportunities
The Master of Science in Electrical Engineering has the following nine streams:
- Computing and Electronics
- Communications and Networks
- Electric Power and Smart Grid Systems
- Control and Automation
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- Internet of Things
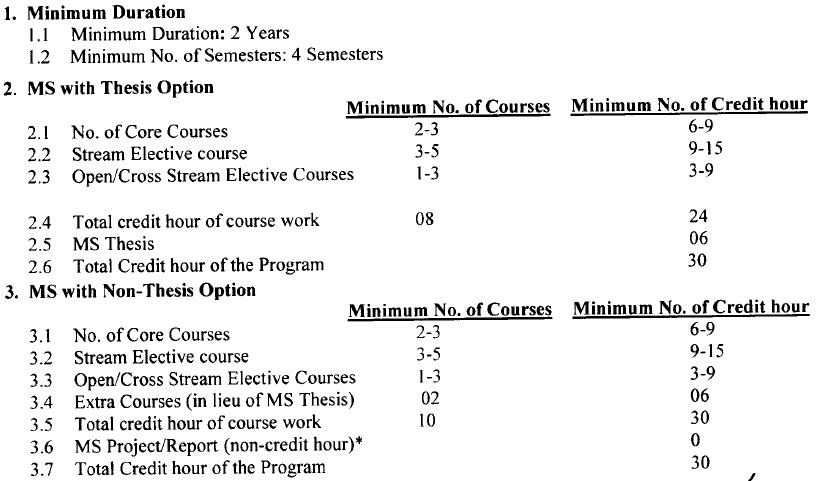
MS Program Structure
- The scholar must complete a minimum of 30 credit hours for MS degree, out of which he/she has to undertake minimum 24 credit hours of course work and 06 credit hours of MS thesis/Research Project.
- The scholar can register a minimum of 03 credit hours and maximum of 12 credit hours in a semester.
- The scholar can register an alternate elective course from the approved list of elective courses of the program in case the failed elective course is not being offered by the respective department.
- The scholar can register for research thesis after completion of 12 credit hours of course work, on the advice of the Supervisor/Supervisory Committee/Graduate Advisory Committee.
Admission Criteria
For MS
- A 16 years degree in the relevant field from an accredited educational institution with First Division (annual system) or CGPA 2.5/4.0 (semester system).
- No third division or D grade throughout the academic career.
- GAT (General) with 50% marks.
Curriculum Overview